- SAM RO
- 0 Comments
What are gliomas and the different types?
Gliomas are a type of tumor that arises from glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. Glial cells provide support and protection to neurons, and there are different types of glial cells, such as astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and ependymal cells. Gliomas can originate from any of these cell types and can be classified based on the specific cell they arise from, as well as other characteristics. The grading of gliomas is based on the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system, ranging from grade I (least aggressive) to grade IV (most aggressive). Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant and aggressive type. Treatment for gliomas often involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, and the approach depends on factors such as the tumor type, grade, and location.
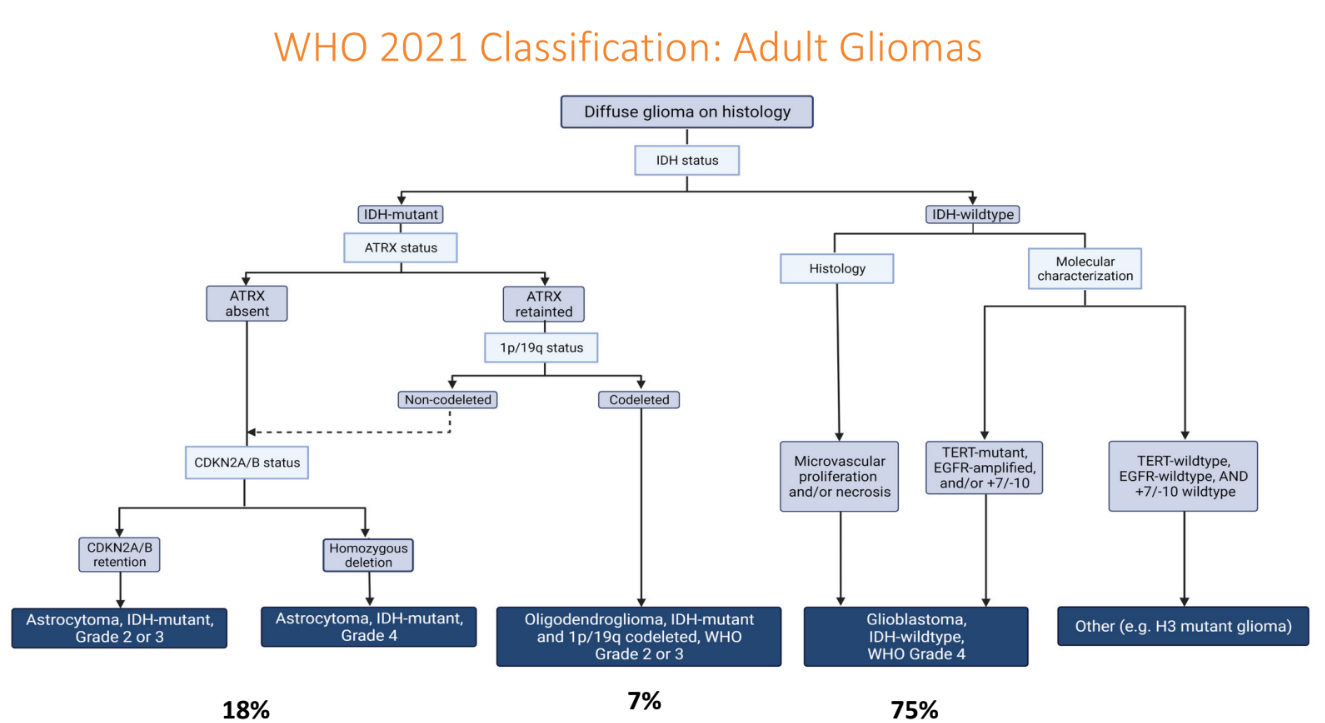
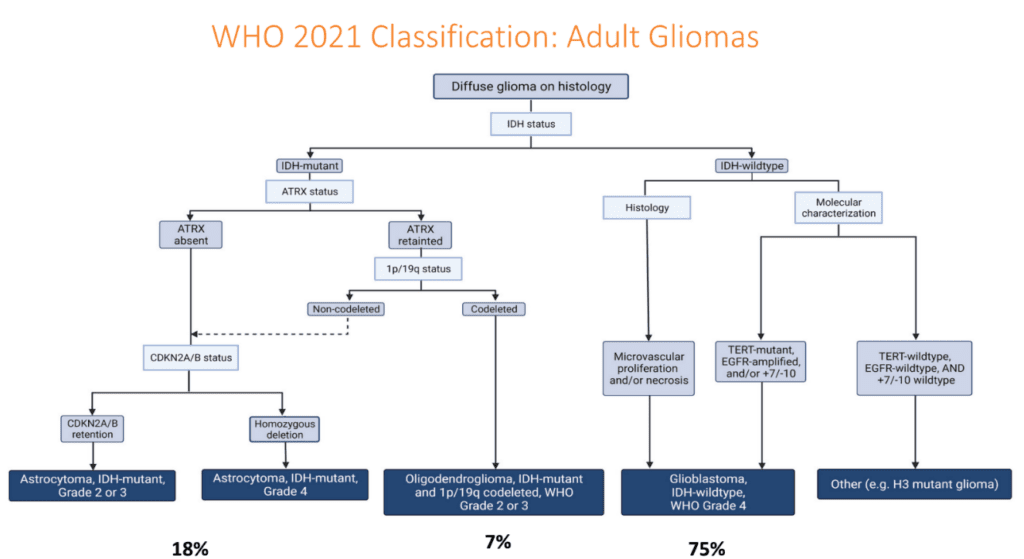
Very often, other than cellular and microscopic appearance, pathologists and doctors need to perform further testing to sub-classify gliomas.
The first step is to ascertain IDH status. IDH (Isocitrate Dehydrogenase) mutation refers to a genetic alteration in the IDH genes, specifically IDH1 (Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1) and IDH2 (Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 2). These mutations are commonly found in certain types of gliomas, particularly in lower-grade gliomas and secondary glioblastomas. Prognosis is more favorable for mutants.
The 1p/19q co-deletion is a specific genetic alteration commonly observed in oligodendrogliomas, a type of glioma. The presence of 1p/19q co-deletion is considered a favorable prognostic marker. These tumours also respond more to chemotherapy than more aggressive gliomas.
For patients who do not have IDH or 1p19q co-deletion, they have a more aggressive form of glioma known as GBM (glioblastoma multiforme). Doctors can check for MGMT methylation result. Patients with MGMT-methylated glioblastomas tend to have a better prognosis and longer overall survival compared to those with unmethylated MGMT. MGMT methylation refers to the epigenetic modification of the MGMT (O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase) gene. Patients with MGMT-methylated glioblastomas tend to have a better prognosis and longer overall survival compared to those with unmethylated MGMT as the tumours are more sensitive to temozolamide, an oral chemotherapy agent taken for GBM.
Sometimes, your doctors may recommend next generation sequencing. NGS results can guide the selection of targeted therapies based on the specific molecular characteristics of the tumor. This approach allows for a more personalized and potentially more effective treatment strategy, as opposed to a one-size-fits-all approach. NGS results may help identify patients who are eligible for specific clinical trials testing novel therapies targeting specific genetic alterations. One commercial test done commonly in Singapore is a local kit developed jointly by several stakeholders (Lucence United)
Gliomas are a spectrum, and while GBM still remains an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, in the future, scientists hope that with precision medicine and molecular profiling, doctors can identify specific genetic mutations and molecular signatures associated with GBM. This information is crucial for developing targeted therapies tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient’s tumor.
Other emerging technologies include tumour-treating fields, nanotechnology and FLASH proton therapy.