Esophageal cancer can be broadly classified into two main types based on the type of cells from which the cancer originates: squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Each type has different risk factors, locations within the esophagus, and treatment approaches.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
- Location: Typically occurs in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus.
- Risk Factors: Associated with factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain dietary factors.
- Treatment Options:
- Surgery: Depending on the stage, surgery may involve removing the tumor, part of the esophagus, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy: Often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy.
- Radiation Therapy: May be used before or after surgery or as a primary treatment.
- Adenocarcinoma:
- Location: Often occurs in the lower part of the esophagus, near the junction with the stomach.
- Risk Factors: Linked to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Barrett’s esophagus.
- Treatment Options:
- Surgery: Similar to squamous cell carcinoma, surgical removal of the tumor and affected tissue is a common approach.
- Chemotherapy: Used before or after surgery, or as the primary treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Employed in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy.
The treatment of esophageal cancer can be in several forms. Treatment plans are often determined through a multidisciplinary approach involving oncologists, surgeons, radiation oncologists, and other specialists.
Esophagectomy: This is the most common surgical procedure for esophageal cancer. It involves the removal of a portion or the entire esophagus. The surgeon may also remove nearby lymph nodes and, in some cases, part of the stomach.
Chemotherapy: can be given before to shrink the tumour or after surgery to eradicate microscopic disease. It is sometimes given for advanced cases to relieve symptoms.
Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Supportive Care and nutritional Support: As esophageal cancer can impact swallowing and nutrition, nutritional support and counseling are often integral parts of the treatment plan.
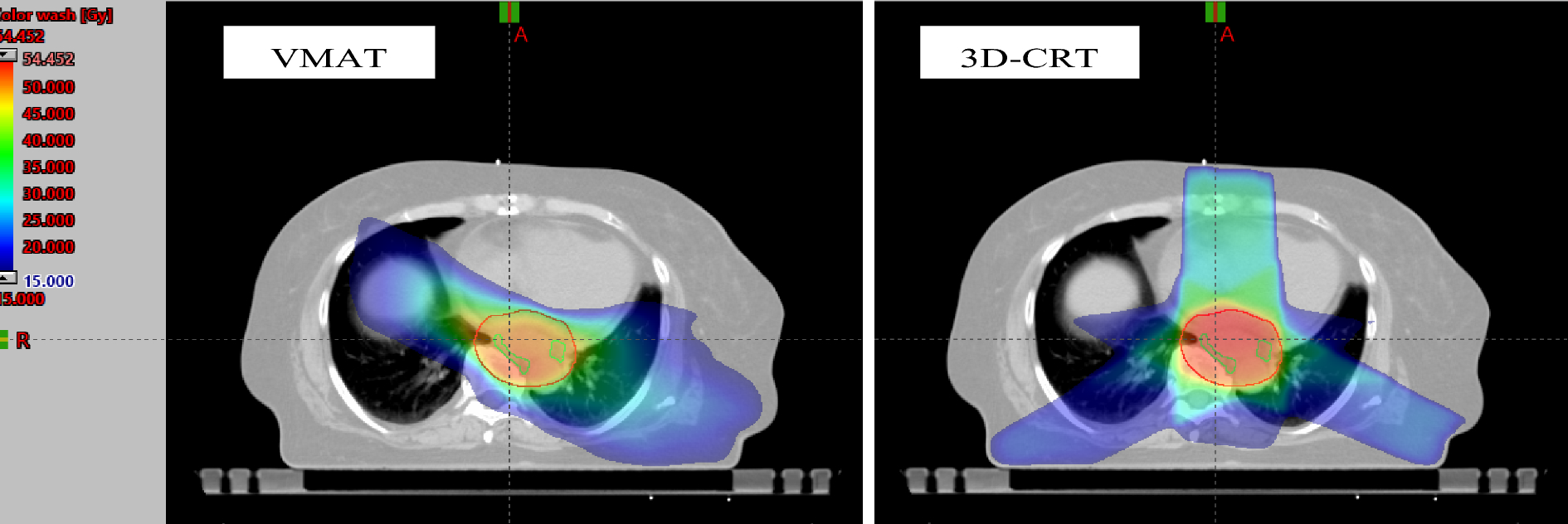
Radiotherapy: In esophageal cancer, radiotherapy is employed to target and destroy cancer cells, either as a primary treatment or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy. It can be used to shrink tumors before surgery, as definitive therapy for localized disease especially for squamous cell variant, or to alleviate symptoms in advanced cases. Proton beam therapy can be useful to reduce lung and heart toxicities.